Wheat and Barley Section, Deptt. of Genetics & Plant Breeding, College of Agriculture, CCS HAU, Hisar-125 004
Dr. Karmal Singh Malik
Mailing Address
Trends in area, production and productivity (50 Years):
In the domain of foodgrains, wheat & barley respectively occupies the first and fourth position in terms of global acreage under food crops. Wheat, the second most important cereal crop is a major source of daily calorie intake. Globally, wheat (Triticum spp.) is grown in about 221.21 million hectares holding the position of highest acreage among all crops with annual production covering around 779.03 million tonnes. In India, it is covering an area of 30.54 million hectares with a production of 106.84 million tonnes and productivity of 3464 kg/ha. Wheat has traditionally been dominated by the NWPZ of India. In Haryana, it occupies an area of 2.47 million hectare with recorded production of 10.62 million tonnes with productivity of 4299 kg/ha (ICAR-IIWBR 2022). After the inception of All India Coordinated Wheat Improvement Project in 1965, wheat production has made a substantial increase and real breakthrough in productivity. Since then, the spectacular advances have been made in yield potential, productivity and sustainability of wheat based systems.
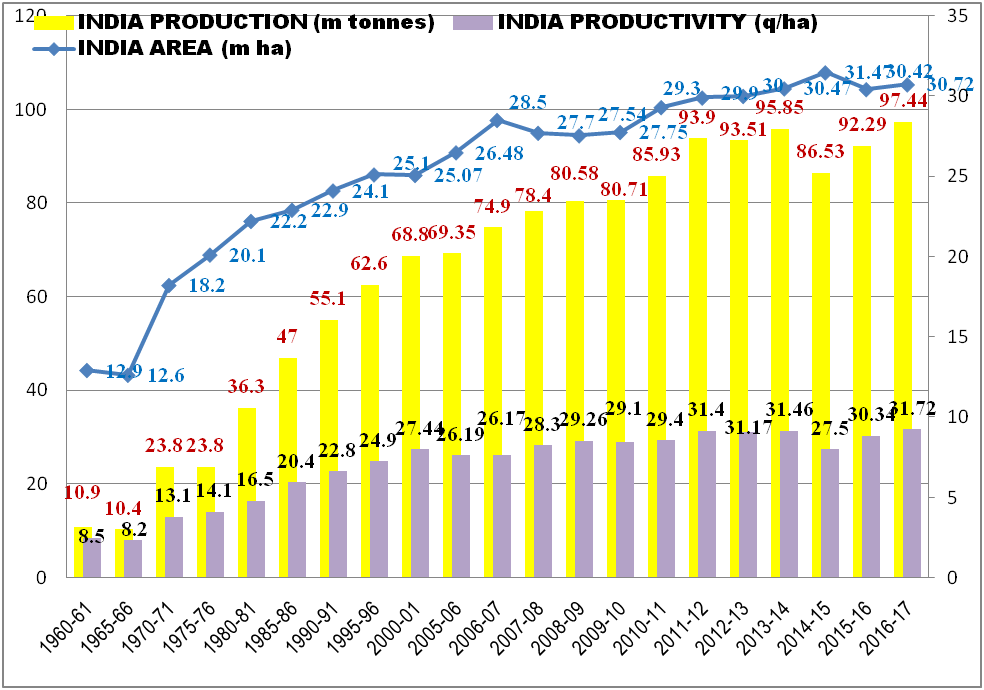
TRENDS IN AREA, PRODUCTION & PRODUCTIVITY OF WHEAT IN INDIA
The country has been divided into five wheat growing zones based on agro-climatic conditions, disease spectrum and soil status (Source: ICAR-IIWBR, 2022).
Table 1: Zone wise area under wheat in India
Zone | Area covered | Approx. Area |
Northern Hills Zone (NHZ) | Western Himalayan regions of J&K (except Jammu and Kathua distt.) H.P. (except Una and Paonta valley); Uttaranchal (except Tarai area); Sikkim and Hills of West Bengal and N.E. states | 0.80 |
North Western Plains zone (NWPZ) | Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Rajasthan (except kota and uadipur divisions) and western U.P. (except Jhansi division), parts of J&K (Jammu and Kathua distt.) and parts of H.P. (Una distt and paonta valley) and Uttaranchal (Tarai region) | 11.1 |
North Eastern Plain zone (NEPZ) | Eastern UP, Bihar, Jharkhand, Orissa, West Bengal, Assam and Plains of N.E. states | 9.2 |
Central zone (CZ) | Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Gujrat, Kota and Udaipur divisions of Rajasthan and Jhansi division of Uttar Pradesh | 5.0 |
Peninsular zone (PZ) | Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Goa, Plains of Tamil Nadu, Hilly areas of Tamil Nadu and Kerala comprising the Niligiri and Palni hills of southern plataeau | 1.6 |
| Total | 27.7 |
However, the two most important zones which account for about 80 per cent of the total wheat area in India, are NWPZ and NEPZ and therefore, the wheat production in the country is mainly dictated by the wheat production in these two zones. The realized wheat yield in NEPZ are considerably lower than potential yield (i.e. <30q/ha). In each of these zones different target environments can be identified for the purpose of varietal improvement programmes.
Target Environment
Wheat breeding in different wheat growing zones is centred to meet the requirements of the following target environments.
1.Timely sown, irrigated areas
2.Late sown, irrigated areas
3.Timely sown, rainfed area
4.Timely sown, restricted irrigation areas
5. Salt affected soils area.
6. Heat-stressed environment
Last Updated :-Sat, May 04 2024
| # | Image | Name | Designation | Specialization | Details |
|---|
| # | Image & Name | Designation | Qualification | Phone |
|---|
Awards and Recognitions
Dr. I. S. Sheoran was awarded Hari Om Ashram award for team research, Rafi Ahmed Kidwai award and NAAS Fellow : -
Infrastructural Development
- The department has a Botanical Garden spread over an area of 10.5 acres with rich biodiversity. The department has done pioneering work in conserving the indigenour local species of plant and also introduction of exotic specis (approximately 600) from other places. Various native and exotic trees, shurbs, herbs, climbers, aquatic plants, cacti and succulents have been collected and maintained for imparting knowledge to our students as well as related scientists. Flower shows are organized from time to time.
- The department has 9 screening houses near the college building.
- The department has developed 20 salinity micro plots to determine phyto-remediating potential of halophytic flora and 24 lysimeter have been installed in field to determine the transpirational potential of trees having importannce in bio-drainage.
- Experimental farms spread over 25 acres have been developed to evaluate bio-drainage potential of trees to improve waterlogged soils.
Package and Practices
system having Eucalyptus tereticornis as a strip plantation should be established on the water logged soils. In this model north to south field boundary is converted into 2.6 m wide and 45 cm high raised bund on which two rows of trees can be planted. The intervening space is left for the crops with minimum of shade effect due to the north-south direction of bunds� initiated by Drs. O.P. Toky, Rajiv Angrish and J.C. Kaushik included in the HAU Package of Practices.
Other Activities of the Department
Van Mahotsav was celebrated at CCS HAU premises in Botanical Garden of the Department of Botany & Plant Physiology On 27th July, 2015. The guest of honour in the function was honourable Agriculture Minister Sh. O.P.Dhankar. The Agriculture Minister, Vice -Chancellor (Dr. K.S.Khokhar), Member of Board (Dr. Ramesh Yadav) & Dean PGS (Dr. Rajbala Grewal) planted Tejpata, Putjeeva, Raintree and Chandni trees in Botanical Gardn.
On 20th August, 2015 tree plantation programme was conducted by the Department of Botany & Plant Physiology, College of Basic Sciences & Humanities in the Botanical Garden. The Deputy Director General (Crop Science) Dr. J.S.Sandhu Guest of Honour planted trees, along with dignitaries Vice -Chancellor (Dr.K.S.Khokhar), Registrar (Dr.M.S.Dahiya), Director of Research (Dr.S.S.Siwach), Dean, COA (Dr. R.K.Pannu) & Dean, COBS&H (Dr.R.KJain). The planted trees were Sacred Ashoka, Kachnar, Dalchini, Ashok and Ficus Sp.
Training/Symposium /Conference Organized
Organized 4 day Third Indian Palynological conference on Palynology in Crop Production & Improvement in Sepetember 21-23, 1981.
Organized 3 day Symposium of Plant Physiology (1984) in collaboration with Indian Society for Plant Physiology, New Delhi.
The Department organized National Level Training Programme on Biodrainaege: Potential and Practice funded by Ministry of Water Resources G.O.I., from Feb 1st to 6th, 2008. Dr. R. Angrish of this Department was the Course Director, held at DHRM, CCS HAU, Hisar.

Phone No : 01662255408, 09812700110
Email Id :hos_wheat@hau.ac.in